What is a water softener?
A water softener is a household system that treats hard water using a process called ion exchange to remove hardness-causing minerals such as calcium and magnesium from your water. These systems are installed at the main water line of your home to treat hard water before it goes through the pipes, appliances, and water heater in your home. Softening your water can prevent common hard water problems like clogged pipes, damage to water-based appliances, and dry or itchy skin and hair from showering.
Do you need a water softener?
Depending on the hardness of your water, different problems can arise in your home. Some are easy to notice right away while others slowly worsen over time. Signs that you have hard water in your home include:
- Spots or streaks on dishware
- Soap scum on shower walls or sinks
- Little soap lather when washing hands
- Clothing color fades quicker
- White spots on clothes
- Stiff towels
- Skin and hair feel dryer
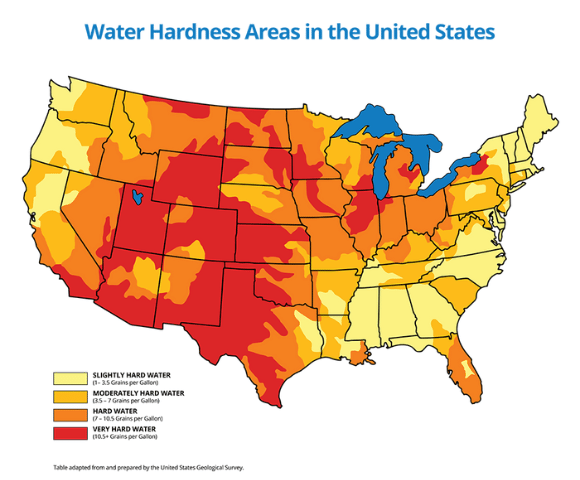
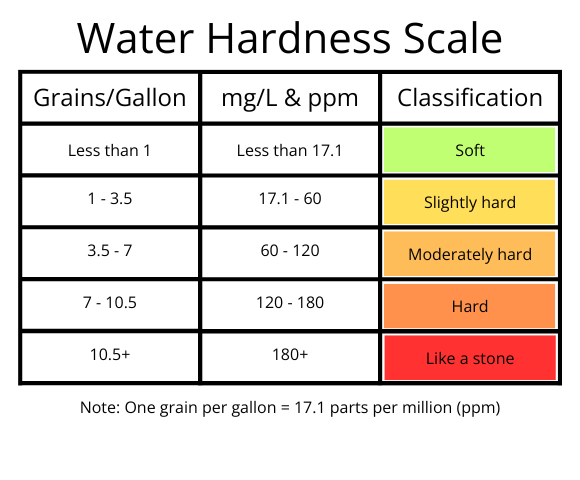
If you want to know for sure if you have hard water, you can check your local water quality report or get your water tested by an independent water company. Water with over 3 grain per gallon (GPG) is considered hard. The higher your GPG number, the harder your water is, and the worse your problems can get.
Types of water softeners
Water softeners can be categorized into two different types: salt-based and salt-free. Let’s talk about each and the different methods they use to soften your water.
Salt-based water softeners
- Single tank salt-based water softeners: The most commonly used softener. You add salt to the tank, which charges resin beads with sodium ions. As hard water passes over the beads, the hard mineral ions get exchanged with those from the beads. The outflowing water is effectively softened because it doesn’t have the hard mineral ions anymore, and the beads get recharged through a process known as regeneration as the softened water flows over them. The downside is that the regeneration process can take a bit of time, and you won’t have softened water during this period. There are several salt-based softener options and they’re typically recommended for those with water that has a high hardness level.
- Dual tank water softeners: A salt-based system with two tanks instead of one. It uses the same ion exchange process as single tank versions, but having two tanks means you don’t need to go without filtered water during the regeneration cycle.

Salt-free water softeners
- Electromagnetic and magnetic: These systems use a magnetic field to strip ions from heavy minerals and neutralize them. This prevents them from being able to stick to surfaces and cause limescale.
- Water conditioners: Water conditioners aren’t actually softeners, but they are systems that help reduce scale buildup. These systems don’t require salt, and instead use technology that inhibits scale buildup by transforming dissolved hard minerals into inactive microscopic crystal particles that are harmlessly passed through your water and down your drain.
Most water softeners and water conditioners can be paired with a whole house water filter so that in addition to softening your water, you’re also tackling other contaminants such as chlorine, chloramines, heavy metals, herbicides, viruses, and bacteria.
Considerations when buying a water softener
Before choosing a water softener, there are things you need to consider to know you’re picking the right one for your home:
Water usage and hardness
The capacity of the water softener you need depends on several factors including the size of your home, water usage and number of water fixtures, and the hardness of your water. Determining your water usage is simple if you follow this formula:
Number of people in the household x 82 gallons of water per day = total household water usage
The average person uses 82 gallons of water per day, so multiplying 82 gallons by the number of people in your household will give you your average water usage. After this, you need to determine your water hardness, which is measured using grains per gallon (GPG). You can find your hardness measure in your local water quality report.Once you find this number, multiply your water hardness x total household water usage to determine your desired water softener size. For example, if a home uses 300 gallons of water per day with a water hardness of 10 GPG, it would need a water softener with a capacity of 3,000 grains per day.
Regeneration method
Salt-based softeners must go through a regeneration cycle whenever their salt content runs low. A regeneration cycle is the process of removing hardness minerals from the softener’s resin beads, recharging them, and flushing out the wastewater. How often this occurs depends on whether you have a time-based or metered regeneration system.
Time-based softeners are automatically set to regenerate at a fixed time. When installing your water softener, you program the time of day so that your softener regenerates at a time when you and your family are not using water, like 2 A.M. This enables the owner to have more control over the regeneration cycle schedule, but at the risk of using more salt than necessary if the intervals are too short. On the other hand, intervals that are too short may result in your pipes being exposed to hard water.
Metered softeners are not on a fixed schedule and work by counting the gallons of water that pass through them. This means your system will only regenerate when it's necessary. However, this gives you less control over when the regeneration cycle occurs. You may find yourself having to wait for regeneration in the middle of cooking dinner which can be an inconvenience.
Convenience features
Although not always necessary, some water softeners offer additional features to improve convenience. These include touch screens, water flow indicators, low salt indicators, and high flow valves. Features like these make it easier to use and maintain your water softener long-term.
Installation and maintenance
It’s important to look into your water softener’s installation and maintenance details to better understand what this process entails and if it’s something you’re comfortable with. Some softeners come with detailed instructions for you to handle yourself, while others require a professional to come out and install them. This also applies to maintenance, which may factor into your decision if it seems like the system will be cumbersome to maintain. If you plan on doing the work yourself, be sure to verify that the brand provides clear instructions and a thorough manual or a video walkthrough.
Contamination removal
Water softeners are your best option for treating hard water problems, but what’s best for you will depend on the needs of your household. If you’re concerned about additional contaminants, you may want to consider a more comprehensive solution like a whole house water filter plus softener or conditioner combination.
Aquasana offers independently-tested, whole-house water filters that reduce 97% of chlorine and more contaminants. Our high-performance filtration systems can work with our SimplySoft® Softeners or Salt-Free Water Conditioner to address hard water and scale buildup.
Shop our water filtration products or contact one of our Water Experts to find the best set-up and configuration for your needs.
WHOLE HOUSE WATER SOFTENER
SimplySoft® 40,000 Grain Softener
Reduces minerals that cause hard water, providing softer, scale-free water from every tap in your home.
.png)


