Advantages of reverse osmosis
The main advantages of reverse osmosis include:
- Removes more contaminants than other filtration methods.
- Filters water down to a sub-micron level.
- Provides the best water for cooking which is why it has become popular among chefs.
Disadvantages of reverse osmosis
Some disadvantages of reverse osmosis include:
- During the process, RO systems produce quite a bit of wastewater; a typical system has a ratio of about 4:1. That’s four gallons wasted for every gallon of clean water produced.
However, there are “zero waste” systems that use electricity to force water through the RO membrane or recycle wastewater, but this puts wear and tear on your system meaning you’ll have to replace filters more often.
- Removes healthy minerals that your body needs including calcium, potassium, and magnesium because they are so effective at removing solids.
To address this, Aquasana’s SmartFlow® Reverse Osmosis Filter utilizes remineralization technology to restore these beneficial minerals and restore water to a good pH balance.
What is carbon filtration?
Most filters on the market use carbon filtration technology to retain contaminants inside your filter, preventing them from flowing through your tap. Carbon filters rely on the process of adsorption, in which the filter acts like a magnet — allowing contaminants to collect on a large surface area where molecules exert force for other molecules to attract to. The longer the water stays in contact with the carbon media, the more contaminants can be absorbed from the water.
There are two main types of carbon filters on the market, including:
- Activated Carbon – The majority of water filters you’ll come across use an activated carbon media made from coconut shell, coal, or wood. These filters are incredibly porous and a single teaspoon has more surface area than a football field enabling it to remove contaminants through adsorption.
- Catalytic Carbon – Catalytic carbon is a class of activated carbon that shares the same base benefits, but also can promote chemical reactions used to further remove chlorine and chloramines from tap water.
Advantages of carbon filtration
Many people wonder if carbon filters remove chlorine and if carbon filters are safe to use. The good news is carbon filters:

- Are extremely effective at removing chlorine which will help improve the taste and safety of your tap water.
- Are passive, meaning you won’t waste water or electricity as water passes through them.
- Require very little maintenance, usually only needing a quick and easy filter swap every couple of months.
Disadvantages of carbon filtration
Carbon filters also come with some disadvantages:
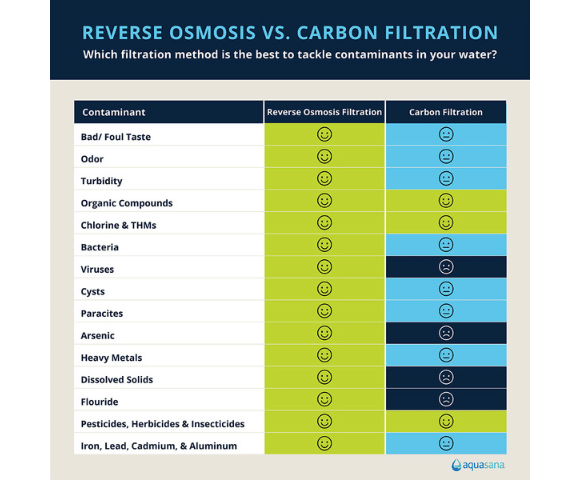
- Activated carbon on its own can’t remove bacteria, viruses, fluoride, heavy metals, or dissolved solids found in tap water.
- Keeping up with carbon filter changes — putting one off may lead to channeling, which reduces the reactions between chemicals and carbon (meaning, it won’t work as well).
Reverse osmosis vs. carbon filters: The difference
Both reverse osmosis and carbon filters have advantages and disadvantages you should consider when choosing a filter for your home.
- Carbon filters: great for removing chlorine which improves safety and taste, but a single-stage carbon filter isn’t enough to sufficiently remove all the contaminants that may be present in tap water.
- Reverse osmosis filters: remove far more contaminants but you’ll lose healthy minerals unless the system you use features remineralization technology to add these back in.
Aquasana’s SmartFlow® Reverse Osmosis utilizes reverse osmosis with carbon filters (both activated and catalytic) along with ion exchange to remove up to 99.99% of 90 contaminants from your water while restoring healthy minerals including calcium.
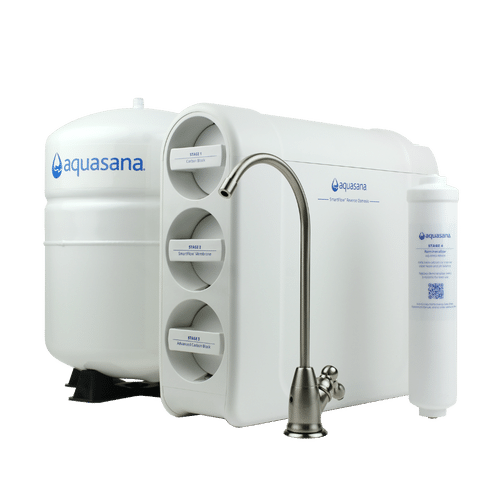
UNDER SINK WATER FILTER
SmartFlow® Reverse Osmosis
High-efficiency reverse osmosis system removes up to 99.99% of 90 contaminants, including fluoride, arsenic, chlorine, and lead.

Whatever you choose, make sure it’s certified
Regardless of whether you choose a reverse osmosis or carbon filter for your home, it’s important to make sure the filter you purchase is certified by a trusted third-party to remove contaminants. That’s where the National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) Certification comes in.
As we’ve previously written, the NSF is a third-party, nonprofit organization that develops standards for and certifies goods including clean water, food, and consumer products. Their goal is to help consumers identify which products are up to their standards, and which ones aren’t.
Before buying any water filter, check for at least one or several of the following NSF/ANSI Standards:
- NSF Standard 42 – Establishes a minimum requirement for water filtration systems to remove a total of three contaminants such as chlorine taste and odor, as well as particulates that may be present in drinking water.
- NSF Standard 53 – Establishes a minimum requirement for water filtration systems to remove a total of 57 contaminants, including lead, mercury, cryptosporidium, giardia, volatile organic chemicals (VOCs), and other harmful contaminants from drinking water. As of 2019, this standard now includes NSF Standard P473 to cover the reduction of PFOA/PFOS.
- NSF Standard 401 – Verifies a water filter can reduce up to 15 emerging contaminants from a list that includes prescription drugs, herbicides, pesticides, and others that have been found at trace levels in drinking water.
- NSF Standard 58 – Specific to reverse osmosis systems, this standard establishes requirements for the reduction of total dissolved solids (TDS) and other contaminants including nitrate, lead, fluoride, and others.

Aquasana: Water filters you can trust
Aquasana has a wide range of under sink and countertop water filters that use carbon filtration and are WQA tested and certified to NSF/ANSI Standards 42, 53 (includes P473), and 401.
If you determine an RO filter is a better fit for your needs, our SmartFlow® Reverse Osmosis is well renowned for its ability to effectively remove contaminants without sacrificing the healthy minerals your body needs, as it’s certified to NSF Standard 58 and features remineralization technology to restore healthy minerals. Check out the system’s page to learn more or contact us for additional questions.